$ do
Swift Custom Types
2019-06-26
Structures
结构体是值类型, 而非引用类型。结构体无处不存在,许多Swift标准类型都是结构体,比如,Array, Int, Float, Double, Bool, Dictionary, Set 和 String都是被定义为结构体。所以它们所有自己的方法和属性。
struct Location {
let x: Int
let y: Int
}
let storeLocation = Location(x: 2, y: 4) // swift 自动提供的初始化函数,强制必须设置所有属性
struct DeliveryArea {
let center: Location // let 不可修改
var radius: Double // var 可修改
}
var storeArea = DeliveryArea(center: storeLocation, radius: 4) // var 可以修改其可修改属性
print(storeArea.radius) // 4.0
print(storeArea.center.x) // 2
storeArea.radius = 250
let fixedArea = DeliveryArea(center: storeLocation, radius: 4) // let 结构体属性不可修改
fixedArea.radius = 250 // Error: Cannot assign to property
// copy-on-assignment 结构体是值类型, 而非引用类型
var area1 = DeliveryArea(center: Location(x: 2, y: 4), radius: 2.5)
var area2 = area1
print(area1.radius) // 2.5
print(area2.radius) // 2.5
area1.radius = 4
print(area1.radius) // 4.0
print(area2.radius) // 2.5Properties
存储属性
struct Contact {
var fullName: String
var emailAddress: String
var relationship = "Friend" //默认属性
}
var person = Contact(fullName: "Grace Murray", emailAddress: "grace@navy.mil")
var person = Contact(
fullName: "Grace Murray",
emailAddress: "grace@navy.mil",
relationship: "Friend"
)计算属性
struct TV {
var height: Double
var width: Double
var diagonal: Int {
let result = (height * height + width * width).squareRoot().rounded()
return Int(result)
}
}
var tv = TV(height: 53.93, width: 95.87)
let size = tv.diagonal // 110
tv.width = tv.height
let diagonal = tv.diagonal // 76Getter and setter
var diagonal: Int {
get {
let result = (height * height + width * width).squareRoot().rounded()
return Int(result)
}
set {
let ratioWidth = 16.0
let ratioHeight = 9.0
let ratioDiagonal = (ratioWidth * ratioWidth + ratioHeight * ratioHeight).squareRoot()
height = Double(newValue) * ratioHeight / ratioDiagonal
width = height * ratioWidth / ratioHeight
}
}
tv.diagonal = 70
let height = tv.height // 34.32...
let width = tv.width // 61.01...type properties
类型属性,跨越实例共享
struct Level {
static var highestLevel = 1 // static 修饰为 type properties
let id: Int
var boss: String
var unlocked: Bool
}
let highestLevel = level3.highestLevel // Error: you can't access a type property on an instance
let highestLevel = Level.highestLevel // 1property obsevers
-
willSet, didSet 仅用于存储属性,计算属性直接使用 getter 和 setter 即可。
-
willSet, didSet 在结构体初始化时不会被调用,只有属性更新新值时才会调用。
struct Level {
static var highestLevel = 1
let id: Int
var boss: String
var unlocked: Bool {
didSet { // obsevers
if unlocked && id > Level.highestLevel {
Level.highestLevel = id
}
}
}
}Limiting a variable
struct LightBulb {
static let maxCurrent = 40
var current = 0 {
didSet {
if current > LightBulb.maxCurrent {
print("""
Current is too high,
falling back to previous setting.
"""
)
current = oldValue
}
}
}
}
var light = LightBulb()
light.current = 50
var current = light.current // 0
light.current = 40
current = light.current // 40Lazy properties
struct Circle {
lazy var pi = { // lazy 属性必须是变量 (var)
return ((4.0 * atan(1.0 / 5.0)) - atan(1.0 / 239.0)) * 4.0
}()
var radius = 0.0
var circumference: Double {
mutating get {
return pi * radius * 2
}
}
init(radius: Double) { // 自定义初始化函数,一旦自定义构造方法,默认构造方法将无效
self.radius = radius
}
}
var circle = Circle(radius: 5) // got a circle, pi has not been run
let circumference = circle.circumference // 31.42 // also, pi now has a valueMethods
func distance(from source: (x: Int, y: Int), to target: (x: Int, y: Int)) -> Double {
let distanceX = Double(source.x - target.x)
let distanceY = Double(source.y - target.y)
return (distanceX * distanceX + distanceY * distanceY).squareRoot()
}
struct DeliveryArea {
let center: Location
var radius: Double
func contains(_ location: Location) -> Bool { // Method
let distanceFromCenter =
distance(from: (center.x, center.y), to: (location.x, location.y))
return distanceFromCenter < radius
}
}
let area = DeliveryArea(center: Location(x: 5, y: 5), radius: 4.5)
let customerLocation = Location(x: 2, y: 2)
area.contains(customerLocation) // trueself
let months = ["January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"]
struct SimpleDate {
var month: String
var day: Int
func monthsUntilWinterBreak() -> Int {
return months.index(of: "December")! - months.index(of: self.month)! // self
// return months.index(of: "December")! - months.index(of: month)! // self 可省略
}
}
date.monthsUntilWinterBreak() // 2Initializers
let date = SimpleDate(month: "January", day: 14) //swift 自动提供的初始化函数,强制必须设置所有属性
let date = SimpleDate(day: 14) // Error!
struct SimpleDate {
var month: String
var day: Int
init(day: Int) { // 自定义初始化函数
month = "January"
self.day = day // 都为 "day",self 不可省
}
func monthsUntilWinterBreak() -> Int {
return months.index(of: "December")! months.index(of: month)!
}
}
let date = SimpleDate(day: 14)
date.month // January
date.monthsUntilWinterBreak() // 11
let date = SimpleDate(month: "February", day: 14) // Error! // 一旦自定义构造方法,默认构造方法将无效mutating methods
-
结构体为值类型, 如果一个方法改变了其属性值, 其实例的值须修改。
-
所以有 mutating 方法的结构体不能实例化为常量。
-
用 mutating 修饰的方法, swift 传入的 self 为一个标记为 inout 的参数。
struct SimpleDate {
var month: String
var day: Int
init(day: Int) {
month = "January"
self.day = day
}
mutating func advance() { // 只有标记了 mutating 的方法才能修改结构体实例的值
day += 1
}
func monthsUntilWinterBreak() -> Int {
return months.index(of: "December")! months.index(of: month)!
}
}type methods
类型方法,跨越实例共享
struct Math { // 可用于 namespace (命名空间)
static func factorial(of number: Int) -> Int {
return (1...number).reduce(1, *)
}
}
Math.factorial(of: 6) // 720Protocol
public protocol CustomStringConvertible {
/// A textual representation of this instance.
public var description: String { get }
}
struct DeliveryArea: CustomStringConvertible {
let center: Location
var radius: Double
var description: String { // 实现协议必须实现其方法
return """
Area with center: x: \(center.x) - y: \(center.y),
radius: \(radius)
"""
}
func contains(_ location: Location) -> Bool { // Method
let distanceFromCenter =
distance(from: (center.x, center.y), to: (location.x, location.y))
return distanceFromCenter < radius
}
}
// print() 调用 description 方法进行输出
print(area1) // Area with center: x: 2 - y: 4, radius: 4.0
print(area2) // Area with center: x: 2 - y: 4, radius: 2.5Extensions
- 不能在 Extensions 中添加存储属性
- 因为添加存储属性会改变被扩展结构体的内存大小,破坏了被扩展结构体
struct Math {
static func factorial(of number: Int) -> Int {
return (1...number).reduce(1, *)
}
}
extension Math {
static func primeFactors(of value: Int) -> [Int] {
var remainingValue = value
var testFactor = 2
var primes: [Int] = []
while testFactor * testFactor <= remainingValue {
if remainingValue % testFactor == 0 {
primes.append(testFactor) remainingValue /= testFactor
} else {
testFactor += 1
}
}
if remainingValue > 1 {
primes.append(remainingValue)
}
return primes
}
}
Math.primeFactors(of: 81) // [3, 3, 3, 3]在 Extension 中添加初始化方法,其结构体自动生成的初始化方法将会保留
struct SimpleDate {
var month: String
var day: Int
func monthsUntilWinterBreak() -> Int {
return months.index(of: "December")! - months.index(of: month)!
}
mutating func advance() {
day += 1
}
}
extension SimpleDate {
init() {
month = "January"
day = 1
}
}Class
类为引用类型
- 结构体是不可变的值类型,类是可变的引用类型
- 类不像结构体,类没有提供默认构造方法,必须要写构造方法显式的给所有属性赋值
- 类通常用来代表对象,结构体用来代表值
- 结构体用栈更快,类用堆较慢
- 需较多的短暂使用的实例用结构体,需较少的长生命周期的实例用类
- 不改变的简单数据存储用结构体,需要更新数据更新状态存储逻辑时用类。尽量先用栈,如果需要添加类的能力时再改为类。
- == 比较值是否相等,=== 比较内存地址是否相等
class Person {
var firstName: String
var lastName: String
init(firstName: String, lastName: String) {
self.firstName = firstName
self.lastName = lastName
}
var fullName: String {
return "\(firstName) \(lastName)"
}
}
let john = Person(firstName: "Johnny", lastName: "Appleseed")
var homeOwner = john
john.firstName = "John" // John wants to use his short name!
john.firstName // "John"
homeOwner.firstName // "John"struct Grade {
let letter: String
let points: Double
let credits: Double
}
class Student {
var firstName: String
var lastName: String
var credits = 0.0
var grades: [Grade] = []
init(firstName: String, lastName: String) {
self.firstName = firstName
self.lastName = lastName
}
func recordGrade(_ grade: Grade) {
grades.append(grade)
credits += grade.credits
}
}
let jane = Student(firstName: "Jane", lastName: "Appleseed")
let history = Grade(letter: "B", points: 9.0, credits: 3.0)
var math = Grade(letter: "A", points: 16.0, credits: 4.0)
jane.recordGrade(history)
jane.recordGrade(math)
jane = Student(firstName: "John", lastName: "Appleseed") // Error: jane is a `let` constant
jane.credits // 7
// The teacher made a mistake; math has 5 credits
math = Grade(letter: "A", points: 20.0, credits: 5.0)
jane.recordGrade(math)
jane.credits // 12, not 8!Extensions
extension Student {
var fullName: String {
return "\(firstName) \(lastName)"
}
}继承
struct Grade {
var letter: Character
var points: Double
var credits: Double
}
class Person {
var firstName: String
var lastName: String
init(firstName: String, lastName: String) {
self.firstName = firstName
self.lastName = lastName
}
}
class Student: Person {
var grades: [Grade] = []
func recordGrade(_ grade: Grade) {
grades.append(grade)
}
}
let john = Person(firstName: "Johnny", lastName: "Appleseed")
let jane = Student(firstName: "Jane", lastName: "Appleseed")
john.firstName // "John"
jane.firstName // "Jane"
let history = Grade(letter: "B", points: 9.0, credits: 3.0)
jane.recordGrade(history)
// john.recordGrade(history) // john is not a student!
class BandMember: Student {
var minimumPracticeTime = 2
}
class OboePlayer: BandMember {
override var minimumPracticeTime: Int { // 重写
get {
return super.minimumPracticeTime * 2
}
set {
super.minimumPracticeTime = newValue / 2
}
}
}final
阻止子类继承
final class FinalStudent: Person {}
class FinalStudentAthlete: FinalStudent {} // Build error!阻止子类重写方法
class AnotherStudent: Person {
final func recordGrade(_ grade: Grade) {}
}
class AnotherStudentAthlete: AnotherStudent {
override func recordGrade(_ grade: Grade) {} // Build error!
}多态
func phonebookName(_ person: Person) -> String {
return "\(person.lastName), \(person.firstName)"
}
let person = Person(firstName: "Johnny", lastName: "Appleseed")
let oboePlayer = OboePlayer(firstName: "Jane", lastName: "Appleseed")
phonebookName(person) // Appleseed, Johnny
phonebookName(oboePlayer) // Appleseed, Jane父子类型转换
var hallMonitor = Student(firstName: "Jill", lastName: "Bananapeel")
hallMonitor = oboePlayer
oboePlayer as Student // 子类转为父类, 编译时期便可确定其正确性
(oboePlayer as Student).minimumPracticeTime // ERROR: 不再是 BandMember, 不能访问其属性
hallMonitor as? BandMember // 父类转子类, 为 Optional, 如果转换失败则为 nil
(hallMonitor as? BandMember)?.minimumPracticeTime // 4 (optional)
hallMonitor as! BandMember // 强制转换, 如果失败, 程序将崩溃
(hallMonitor as! BandMember).minimumPracticeTime // 4 (force unwrapped)
if let hallMonitor = hallMonitor as? BandMember { // 使用 if let
print("This hall monitor is a band member and practices at least \(hallMonitor.minimumPracticeTime) hours per week.")
}static dispatch
子类转为父类的使用场景
func afterClassActivity(for student: Student) -> String {
return "Goes home!"
}
func afterClassActivity(for student: BandMember) -> String {
return "Goes to practice!"
}
// Swift’s dispatch rules: 调用类型最精确匹配的方法
afterClassActivity(for: oboePlayer) // Goes to practice!
afterClassActivity(for: oboePlayer as Student) // Goes home!Override
class StudentAthlete: Student {
var failedClasses: [Grade] = []
override func recordGrade(_ grade: Grade) { // 重写方法,必须要用 Override 修饰
super.recordGrade(grade) // super 调用父类方法
if grade.letter == "F" {
failedClasses.append(grade)
}
}
var isEligible: Bool {
return failedClasses.count < 3
}
}生命周期
初始化
class StudentAthlete: Student {
var sports: [String]
init(sports: [String]) {
self.sports = sports
// Build error - super.init isn’t called before
// returning from initializer
}
}
class StudentAthlete: Student {
var sports: [String]
init(firstName: String, lastName: String, sports: [String]) {
self.sports = sports
super.init(firstName: firstName, lastName: lastName)
}
}- Phase 1: 由子类到父类初始化所有存储属性,直到此阶段完成,才能使用属性和方法
- Phase2: 可以使用属性和方法,并且也可以使用 self
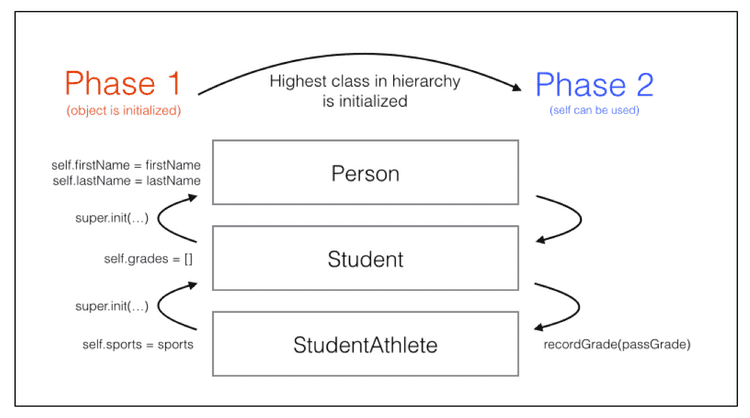
class StudentAthlete: Student {
var sports: [String]
init(firstName: String, lastName: String, sports: [String]) {
self.sports = sports // phase 1
let passGrade = Grade(letter: "P", points: 0.0, credits: 0.0) // 可以创建局部属性,但不能调用属性和方法
super.init(firstName: firstName, lastName: lastName) // 完成后进入 phase 2
recordGrade(passGrade) // phase 2, 可以使用属性和方法以及 self
}
}required
class Student {
let firstName: String
let lastName: String
var grades: [Grade] = []
required init(firstName: String, lastName: String) { // 强制所有子类必须重写
self.firstName = firstName
self.lastName = lastName
}
init(transfer: Student) {
self.firstName = transfer.firstName
self.lastName = transfer.lastName
}
func recordGrade(_ grade: Grade) {
grades.append(grade)
}
}
class StudentAthlete: Student {
// Now required by the compiler!
required init(firstName: String, lastName: String) { // 有 required 修饰,Override 可省略
self.sports = []
super.init(firstName: firstName, lastName: lastName)
}
...
}convenience
class Student {
let firstName: String
let lastName: String
var grades: [Grade] = []
required init(firstName: String, lastName: String) {
self.firstName = firstName
self.lastName = lastName
}
convenience init(transfer: Student) { // convenience 强制直接或间接调用其他 non-convenience initializer
self.init(firstName: transfer.firstName, lastName: transfer.lastName)
}
func recordGrade(_ grade: Grade) {
grades.append(grade)
}
}析构 (deinitializer)
- 非必须, 自动被 swift 调用
- 不能被重写, 内部不能调用 super
- swift 确保会在每个类析构时调用 deinit
- 经常用于一些清理类型的工作
class Person {
...
deinit {
print("\(firstName) \(lastName) is being removed from memory!")
}
}引用计数
automatic reference counting (ARC)
Swift 编译器在编译期间会自动添加增减引用计数的方法调用
var someone = Person(firstName: "Johnny", lastName: "Appleseed")
// Person object has a reference count of 1 (someone variable)
var anotherSomeone: Person? = someone
// Reference count 2 (someone, anotherSomeone)
var lotsOfPeople = [someone, someone, anotherSomeone, someone]
// Reference count 6 (someone, anotherSomeone, 4 references in lotsOfPeople)
anotherSomeone = nil
// Reference count 5 (someone, 4 references in lotsOfPeople)
lotsOfPeople = []
// Reference count 1 (someone)
someone = Person(firstName: "Johnny", lastName: "Appleseed")
// Reference count 0 for the original Person object!
// Variable someone now references a new object循环引用
class Student: Person {
var partner: Student?
...
deinit {
print("\(firstName) is being deallocated!") }
}
var alice: Student? = Student(firstName: "Alice", lastName: "Appleseed")
var bob: Student? = Student(firstName: "Bob", lastName: "Appleseed")
alice?.partner = bob
bob?.partner = alice
alice = nil
bob = nil
// deinit 并没有调用弱引用
class Student: Person {
weak var partner: Student?
...
}Enumerations
enum Month {
case january
case february
case march
case april
case may
case june
case july
case august
case september
case october
case november
case december
}
// 等价于
enum Month {
case january, february, march, april, may, june, july, august, september, october, november, december
}
func semester(for month: Month) -> String {
switch month {
case Month.august, Month.september, Month.october, Month.november, Month.december:
return "Autumn"
case Month.january, Month.february, Month.march, Month.april, Month.may:
return "Spring"
default:
return "Not in the school year"
}
}
// 等价于
func semester(for month: Month) -> String {
switch month {
case .august, .september, .october, .november, .december:
return "Autumn"
case .january, .february, .march, .april, .may:
return "Spring"
default:
return "Not in the school year"
}
}
var month = Month.april
semester(for: month) // "Spring"
month = .september
semester(for: month) // "Autumn"- 枚举有有限个值, switch 只要对这些值有全面处理,可以没有 default, 否则必须要有 default 保证全面的条件处理
- 枚举,全面条件处理不用 default,会有另一个好处:当枚举增加或减少枚举项时,swift 编译器会报错提醒你需要修改 switch
func semester(for month: Month) -> String {
switch month {
case .august, .september, .october, .november, .december:
return "Autumn"
case .january, .february, .march, .april, .may:
return "Spring"
case .june, .july:
return "Summer"
}
}Raw values
- swift 枚举项默认的 Raw values 并不是 integer, 与 C 语言不同
- 但是你可以手动指定 Raw values
enum Month: Int { // 指定为 Int, 也可以是 String, Float, Character 等
// january 为 0, 其他依次递增
case january, february, march, april, may, june, july, august, september, october, november, december
}
enum Month: Int {
// 指定 january 为 1, 其他依次递增
case january=1, february, march, april, may, june, july, august, september, october, november, december
}
enum Coin: Int {
case penny = 1
case nickel = 5
case dime = 10
case quarter = 25
}
let coin = Coin.quarter
coin.rawValue // 25访问 Raw value
func monthsUntilWinterBreak(from month: Month) -> Int {
return Month.december.rawValue - month.rawValue // 访问 Raw value
}
monthsUntilWinterBreak(from: .april) // 8用 Raw value 初始化枚举
let fifthMonth = Month(rawValue: 5) // 不能保证存在此 rawValue 的枚举,故返回 optional
monthsUntilWinterBreak(from: fifthMonth) // Error: not unwrapped
let fifthMonth = Month(rawValue: 5)!
monthsUntilWinterBreak(from: fifthMonth) // 7String raw values
enum Icon: String { // 指定为 String
// 如果不指定,默认自动为与枚举项名称相同的字符串
case music
case sports
case weather
var filename: String {
return "\(rawValue).png"
}
}
let icon = Icon.weather
icon.filename // weather.pngAssociated values
- 每个枚举 case 可以有0个或多个关联值(Associated values)
- 每个枚举 case的关联值都可以有自己的数据类型
- 可以像命名函数参数那样命名关联值
- 一个枚举不能同时有 Raw values 或 Associated values
var balance = 100
enum WithdrawalResult {
case Success(Int)
case Error(String)
}
func withdraw(amount: Int) -> WithdrawalResult {
if amount <= balance {
balance -= amount
return .Success(balance)
} else {
return .Error("Not enough money!")
}
}
let result = withdraw(99)
switch result {
case let .Success(newBalance):
print("Your new balance is: \(newBalance)")
case let .Error(message):
print(message)
}
// Your new balance is: 1与 if case 或 guard case 一起使用
enum HTTPMethod {
case GET
case POST(String)
}
let request = HTTPMethod.post(body: "Hi there")
guard case .post(let body) = request else { // guard case, 是否 request 包含 post 枚举项, 包含则绑定关联值
fatalError("No message was posted")
}
print(body) // 打印关联值枚举可以用作 状态机 ( state machine )
enum TrafficLight {
case Red, Yellow, Green
}
let trafficLight = TrafficLight.Red遍历
enum Pet: CaseIterable {
case cat, dog, bird, turtle, fish, hamster
}
for pet in Pet.allCases {
print(pet)
}用枚举做命名空间
- 结构体可以有相同用法,但结构体可以创建实例,命名空间不需要创建实例,所以用枚举实现命名空间会更好
- 创建枚举实例必须指定枚举项,没有枚举项的枚举便不能创建实例
enum Math {
static func factorial(of number: Int) -> Int {
return (1...number).reduce(1, *)
}
}
let factorial = Math.factorial(of: 6) // 720
let math = Math() // ERROR: No accessible initializersOptional
Optionals 就是用关联值的枚举
var age: Int?
age = 17
age = nil
switch age {
case .none:
print("No value")
case .some(let value):
print("Got a value: \(value)")
}
let optionalNil: Int? = .none
optionalNil == nil // true
optionalNil == .none // trueProtocols
protocol Vehicle {
func accelerate()
func stop()
}
class Unicycle: Vehicle { //实现 Vehicle 协议,必须实现其所有方法
var peddling = false
func accelerate() {
peddling = true
}
func stop() {
peddling = false
}
}Methods
enum Direction {
case left
case right
}
protocol DirectionalVehicle {
func accelerate()
func stop()
func turn(_ direction: Direction)
func description() -> String
}协议 Methods 不能有任何有关实现的代码,包括默认参数
protocol OptionalDirectionVehicle {
// Build error!
func turn(_ direction: Direction = .left)
}
// 需要用重载实现
protocol OptionalDirectionVehicle {
func turn()
func turn(_ direction: Direction)
}Properties
- 需要明确指定属性是 get 还是 set
- 不能包含任何属性的实现代码
- 可以用计算属性或存储属性去实现
protocol VehicleProperties {
var weight: Int { get }
var name: String { get set }
}初始化
protocol Account {
var value: Double { get set }
init(initialAmount: Double)
init?(transferAccount: Account)
}
class BitcoinAccount: Account {
var value: Double
required init(initialAmount: Double) {
value = initialAmount
}
required init?(transferAccount: Account) {
guard transferAccount.value > 0.0 else {
return nil
}
value = transferAccount.value
}
}
var accountType: Account.Type = BitcoinAccount.self
let account = accountType.init(initialAmount: 30.00)
let transferAccount = accountType.init(transferAccount: account)!继承
protocol WheeledVehicle: Vehicle {
var numberOfWheels: Int { get }
var wheelSize: Double { get set }
}实现协议
class Bike: Vehicle {
var peddling = false
var brakesApplied = false
func accelerate() {
peddling = true
brakesApplied = false
}
func stop() {
peddling = false
brakesApplied = true
}
}实现属性
实现 { get } 的属性
- 存储属性常量
- 存储属性变量
- 只读计算属性
- 可读可写计算属性
实现 { get set } 的属性
- 存储属性变量
- 可读可写计算属性
class Bike: WheeledVehicle {
// 实现属性
let numberOfWheels = 2
var wheelSize = 16.0
var peddling = false
var brakesApplied = false
func accelerate() {
peddling = true
brakesApplied = false
}
func stop() {
peddling = false
brakesApplied = true
}
}Associated types
- 只是简单声明一个类型,需在协议中使用
- 不限制类型是什么,实现类来决定
protocol WeightCalculatable {
associatedtype WeightType
var weight: WeightType { get }
}
class HeavyThing: WeightCalculatable {
// This heavy thing only needs integer accuracy
typealias WeightType = Int // 由于类型推导,可省略
var weight: Int {
return 100
}
}
class LightThing: WeightCalculatable {
// This light thing needs decimal places
typealias WeightType = Double // 由于类型推导,可省略
var weight: Double {
return 0.0025
}
}
// 因为 associatedtype 没有确定,WeightCalculatable 不能用于变量声明
let weightedThing: WeightCalculatable = LightThing() // Build error!实现多个协议
protocol Wheeled {
var numberOfWheels: Int { get }
var wheelSize: Double { get set }
}
class Bike: Vehicle, Wheeled {
// Implement both Vehicle and Wheeled
}protocol composition
func roundAndRound(transportation: Vehicle & Wheeled) { // 类型需要同时实现 Vehicle 和 Wheeled 协议
transportation.stop()
print("The brakes are being applied to \(transportation.numberOfWheels) wheels.")
}
roundAndRound(transportation: Bike()) // The brakes are being applied to 2 wheels.用扩展实现协议
可以扩展 swift 标准库里的类型来实现协议
protocol Reflective {
var typeName: String { get }
}
extension String: Reflective {
var typeName: String {
return "I'm a String"
}
}
let title = "Swift Apprentice!"
title.typeName // I'm a String- 可以用扩展将代码按照协议实现来分组,使代码更条理
- 如要移除协议实现只需删掉相应的扩展即可
- 因扩展里不能添加存储属性,只能在原来类型里存储,所以完全在扩展里实现协议是不可能的
class AnotherBike: Wheeled {
var peddling = false
let numberOfWheels = 2
var wheelSize = 16.0
}
extension AnotherBike: Vehicle {
func accelerate() {
peddling = true
}
func stop() {
peddling = false
}
}实现协议类型
- 值类型 ( structs, enums ) 实现协议
- 引用类型 ( class ) 可实现协议
- 用协议声明的变量是值类型还是引用类型需要运行时动态确定
- 可以指定来限制实现的类型
protocol Named {
var name: String { get set }
}
class ClassyName: Named {
var name: String
init(name: String) {
self.name = name
}
}
struct StructyName: Named {
var name: String
}
// 引用类型
var named: Named = ClassyName(name: "Classy")
var copy = named
named.name = "Still Classy"
named.name // Still Classy
copy.name // Still Classy
// 值类型
named = StructyName(name: "Structy")
copy = named
named.name = "Still Structy?"
named.name // Still Structy?
copy.name // Structy
// 指定实现类型必须为 class,此时协议类型确定为引用类型
protocol Named: class {
var name: String { get set }
}标准库中的协议
Equatable
protocol Equatable {
static func ==(lhs: Self, rhs: Self) -> Bool
}class Record {
var wins: Int
var losses: Int
init(wins: Int, losses: Int) {
self.wins = wins
self.losses = losses
}
}
let recordA = Record(wins: 10, losses: 5)
let recordB = Record(wins: 10, losses: 5)
recordA == recordB // Build error!
extension Record: Equatable {
static func ==(lhs: Record, rhs: Record) -> Bool {
return lhs.wins == rhs.wins && lhs.losses == rhs.losses
}
}
recordA == recordB // trueComparable
protocol Comparable: Equatable {
static func <(lhs: Self, rhs: Self) -> Bool
static func <=(lhs: Self, rhs: Self) -> Bool
static func >=(lhs: Self, rhs: Self) -> Bool
static func >(lhs: Self, rhs: Self) -> Bool
}extension Record: Comparable {
static func <(lhs: Record, rhs: Record) -> Bool {
if lhs.wins == rhs.wins {
return lhs.losses > rhs.losses
}
return lhs.wins < rhs.wins
}
}
// 实现了 Equatable 和 Comparable 就可以解锁很方法,如: sort, max, min, starts, contains 等
let teamA = Record(wins: 14, losses: 11)
let teamB = Record(wins: 23, losses: 8)
let teamC = Record(wins: 23, losses: 9)
var leagueRecords = [teamA, teamB, teamC]
leagueRecords.sort()
// {wins 14, losses 11}
// {wins 23, losses 9}
// {wins 23, losses 8}
leagueRecords.max() // {wins 23, losses 8}
leagueRecords.min() // {wins 14, losses 11}
leagueRecords.starts(with: [teamA, teamC]) // true
leagueRecords.contains(teamA) // trueHashable
- 用于字典的 key 或 Set 中的元素时, 必须实现此协议
- 值类型会自动实现 Equatable 和 Hashable
- 引用类型需要自己实现
- hash 值用于在集合中快速搜索
class Student {
let email: String
let firstName: String
let lastName: String
init(email: String, firstName: String, lastName: String) {
self.email = email
self.firstName = firstName
self.lastName = lastName
}
}
extension Student: Hashable {
static func ==(lhs: Student, rhs: Student) -> Bool {
return lhs.email == rhs.email &&
lhs.firstName == rhs.firstName &&
lhs.lastName == rhs.lastName
}
func hash(into hasher: inout Hasher) {
hasher.combine(email)
hasher.combine(firstName)
hasher.combine(lastName)
}
}
let john = Student(email: "johnny.appleseed@apple.com", firstName: "Johnny", lastName: "Appleseed")
let lockerMap = [john: "14B"]CustomStringConvertible
protocol CustomStringConvertible {
var description: String { get }
}print(john) // Student
extension Student: CustomStringConvertible {
var description: String {
return "\(firstName) \(lastName)"
}
}
print(john) // Johnny AppleseedGenerics
Values defined by other values
enum PetKind {
case cat
case dog
}
struct KeeperKind {
var keeperOf: PetKind
}
let catKeeper = KeeperKind(keeperOf: .cat)
let dogKeeper = KeeperKind(keeperOf: .dog)Types defined by other types
class Cat {}
class Dog {}
class Keeper<Animal> {}
var aCatKeeper = Keeper<Cat>()
var aDogKeeper = Keeper<Dog>()
var aKeeper = Keeper() // compile-time error!class Cat {
var name: String
init(name: String) {
self.name = name
}
}
class Dog {
var name: String
init(name: String) {
self.name = name
}
}
class Keeper<Animal> {
var name: String
var morningCare: Animal
var afternoonCare: Animal
init(name: String, morningCare: Animal, afternoonCare: Animal) {
self.name = name
self.morningCare = morningCare
self.afternoonCare = afternoonCare
}
}
let jason = Keeper(name: "Jason", morningCare: Cat(name: "Whiskers"), afternoonCare: Cat(name: "Sleepy"))Type constraints
protocol Pet {
var name: String { get }
}
extension Cat: Pet {}
extension Dog: Pet {}
class Keeper<Animal: Pet> {
...
}where
extension Array where Element: Cat {
func meow() {
forEach {
print("\($0.name) says meow!")
}
}
}protocol Meowable {
func meow()
}
extension Cat: Meowable {
func meow() {
print("\(self.name) says meow!")
}
}
extension Array: Meowable where Element: Meowable {
func meow() {
forEach { $0.meow() }
}
}可用泛型的类型
Array
let animalAges: [Int] = [2,5,7,9]
// 等价于
let animalAges: Array<Int> = [2,5,7,9]
let array = [Int]()
// 等价于
let array = Array<Int>()Dictionary
struct Dictionary<Key: Hashable, Value>let intNames: Dictionary<Int, String> = [42: "forty-two"]
let intNames2: [Int: String] = [42: "forty-two", 7: "seven"]
let intNames3 = [42: "forty-two", 7: "seven"] // 类型推导Optional
enum OptionalDate {
case none
case some(Date)
}
enum OptionalString {
case none
case some(String)
}
struct FormResults {
// other properties here
var birthday: OptionalDate
var lastName: OptionalString
}
enum Optional<Wrapped> { // swift 内部 Optional 的近似实现
case none
case some(Wrapped)
}
var birthdate: Optional<Date> = .none
if birthdate == .none {
// no birthdate
}
var birthdate: Date? = nil
if birthdate == nil {
// no birthdate
}Generic function parameters
func swapped<T, U>(_ x: T, _ y: U) -> (U, T) {
return (y, x)
}
swapped(33, "Jay")
// returns ("Jay", 33)